Getting started
This guide will help you quickly add TalkJS to your React app and create a chat between two users. It uses TalkJS's React SDK, which provides highly customizable chat UI components for your application. We'll use it alongside the JavaScript Data API, which we'll use for data manipulation tasks like synchronizing users and conversations.
In the guide we'll walk you through installing TalkJS, viewing an existing conversation, creating new users and conversations, customizing the UI, and properly securing it all.
To make the most of this guide, you will need:
- A TalkJS account
- Basic familiarity with React
- A React app to which you'd like to add TalkJS chat. If you don't have a React app yet, a build tool such as Vite can offer you a quick way to get started
To get started, install @talkjs/react-components and @talkjs/core:
To view an existing sample conversation, import the Chatbox component, theme, and the related styling into the component where you want to have your chat UI:
Next, add the Chatbox component:
The Chatbox component here takes the following props:
appId: Your TalkJS app ID. You can find your app ID on the Settings page of your TalkJS dashboard. For this guide, use the app ID for your test mode, which has built-in sample users and conversations.
userId: An identifier for the current user to send messages as. This example uses the ID of an existing sample user,sample_user_alice.conversationId: An identifier of the conversation that you want to view. This example uses the ID for a built-in sample conversation,sample_conversation.
The chatbox is wrapped in a divider that applies CSS styling to set the size of the chatbox. You can modify the size to suit your needs.
Run your app. You should get something like the following:
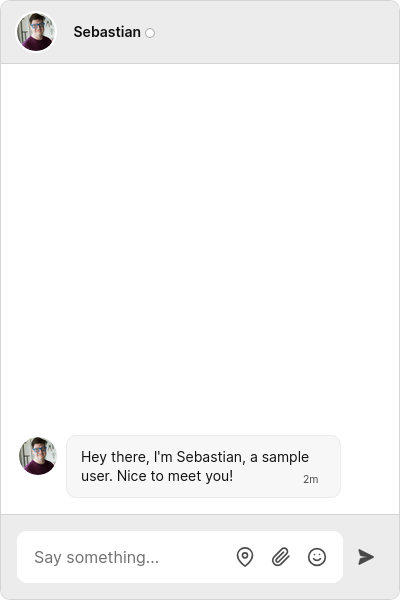
You now have a fully-featured chat window running in your app. Try sending a message!
To view the conversation as a different user, change the userId. For example, try switching the userId to sample_user_sebastian to view the other side of the sample conversation.
If you don't see the chat window, make sure that you've entered your app ID correctly.
So far in this guide we've used a sample user and conversation. Next, we'll create new users and a conversation between them, and sync them with the TalkJS servers. To do this, we'll use the JavaScript Data API which you've already installed earlier through the @talkjs/core NPM package.
Import getTalkSession from the @talkjs/core package into your component, along with React's useEffect:
Add the following code to your component:
This code creates a new TalkJS session, which provides access to a continuous, up-to-date flow of your TalkJS data. It then creates two new users and a conversation between them.
Here's a component with the code so far, so that you can see how it all fits together:
The easiest way to customize TalkJS's components, is using the props and events that the components expose. See each component’s reference documentation for a list of available props.
As an example if you want to hide the built-in chat header, because it doesn't work well with the rest of your UI, you'd render the chatbox like this:
If you need even more flexibility, TalkJS has an extensive theme system, which lets you adapt the styles, markup and behavior of the entire chat UI. See the Customization guide for more details.
Once you're using TalkJS in production you'll need to enable authentication, so that only legitimate users can connect to your chat. You'll need a backend server that can generate tokens for your users to authenticate with. See our Authentication docs for more detail on how to set this up.
To pass the token to your chatbox, add the token prop:
You also need to pass the token to your session:
The token is different each time you connect to TalkJS, so you'll need to call your backend to generate it.
Once you are happy that your chat is loading without errors when you provide a token, go the the Settings page of your dashboard and enable the Authentication (identity verification) option in the Security settings section. When authentication is enabled, only users with a valid token can connect to your chat.
For more ways to customize your chat, see our Chatbox reference docs.